
A person is exposed to the risk of infection by various parasites throughout his life. The most common are helminths (worms in humans). These parasites lead to many complications in the human body, including disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, physical damage to internal organs, and helminthiasis. Helminthiasis is not a disease, but a group of diseases caused by parasites living in humans. All helminths are divided into three main types:
- nematodes (belonging to the order of roundworms), prominent representatives - roundworms, roundworms, whipworms;
- tapeworms or cestodes (order of flatworms) are represented by tapeworms, cattle tapeworms;
- flukes or trematodes (order of flatworms) are represented by flukes.
Since worms leave the body of the host during the reproductive period to preserve the species, transferring to another host or the environment, they are also divided according to the type of transmission:
- Mechanical transmission involves movement over long distances, while no worms form in the body of the carrier. These include most arthropods (crustaceans, arachnids, and millipedes), which are often carried on the legs of common flies.
- The intermediate host is a specific mode of transmission in which one of the stages of development occurs in the body of the vector. For example, for cattle tapeworm, the carrier (intermediate host) is cattle, and humans are the ultimate carriers.
Helminths also differ in their mode of transmission:
- active (contact);
- passive (food).
Contact helminths can enter the human body through the mucous membrane and skin (schitosomes, hookworms). More common are foodborne illnesses that develop after eating unwashed food, coming into contact with a sick person or not following personal hygiene rules.
In total, more than 250 species of lower order worms parasitize humans in the world. Since the symptoms of the presence of worms in people show different manifestations, at the slightest suspicion, a specialist should be consulted and tested.
The life cycle of worms, their reproduction and development
An example of the development of helminths is the classic diagram of the life cycle of a roundworm. The parasite's eggs are extremely resistant to external harmful effects and can remain in the soil for up to six months. The development of the larva itself lasts from 2 weeks to 2 months, depending on the environmental conditions: temperature, humidity, oxygen supply. The mature egg enters the stomach with the food, where the gastric juice eats away the shell of the egg and releases the larva.
After that, the intestinal worm enters the bloodstream through the intestinal wall and begins to move throughout the blood vessel system until it enters the alveoli of the lungs. The roundworm larva is aerobic, only here it becomes active and continues to develop. Feeding on blood, it grows to a length of 3-4 mm. After reaching primary maturity 4-5 days after invasion, the roundworm begins to move toward the bronchi. Its movement causes a cough in humans, as a result of which the larva enters the oral cavity together with the mucous membrane and then again into the intestines. This is where the final stage of larval development occurs.
The life cycle of an adult roundworm lasts about a year, during which time it lays up to 250, 000 eggs. Human health, and sometimes even life, directly depends on the presence and quantity of worms in the body, so it is important to start treatment as early as possible. Ascariasis is accompanied by poisoning, and its complication will be intestinal obstruction, which in some cases requires urgent surgical intervention.
Helminths reproduce in 2 ways, based on which worms are divided into biohelminths and geohelminths. Parasite eggs are usually released into the external environment where they mature. The egg must then enter the host, where it either fully develops (geohelminths) or passes through the stage of transformation into a larva (biohelminths).
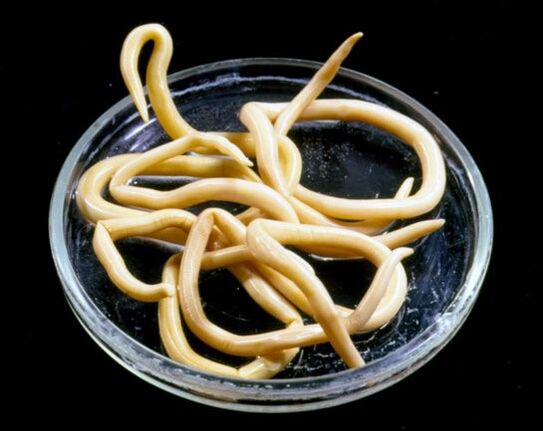

The development process of biohelminths is more complex, the stages of development into an adult and maturity are separate from the stage of larval emergence. That is, from the external environment, the egg is first transferred to an intermediate carrier, where the larva hatches. It must then be ingested by its final host to reach its adult form. Sometimes biohelminths exchange up to 4 intermediate hosts before reaching their final host.
Symptoms
How to determine the presence of worms? The absence of polymorphous symptoms and painful sensations complicates the diagnosis in the first stage of the disease. The causes of the appearance of worms in humans are often related to the consumption of stale or contaminated food, and the parasites themselves live directly in the gastrointestinal tract, so the signs of their presence in the human body in most cases relate to the functioning of the intestinal system. intestines:
- loose (unstable) stools;
- pain and bloating;
- allergic skin rashes;
- bloating;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- loss of appetite or excessive appetite;
- at night - sleep disturbances, vomiting, teeth grinding, salivation;
- itching in the anus;
- the presence of mucus or blood in the stool.
These symptoms appear after infection and last for a short time (about 7 days). In case of re-infection, it will be repeated after 2-3 weeks. In the absence of treatment or due to the occurrence of an acute or chronic form of the disease, some symptoms do not disappear, and the consequences of the long stay of the parasites in the body are added:
- Poisoning occurs almost simultaneously with infection, but is not so noticeable in the early stages. The greater the number of worms in the human body, the stronger the symptoms of poisoning - from morning sickness to vomiting and abdominal pain.
- Congestion in the lungs (infiltrates), bronchospasm, pneumonia. The main culprits are parasites that develop in the alveoli of the lungs and damage them, which triggers inflammatory processes.
- Inflammation of the heart muscle (myocarditis). An infectious disease, the result of the vital activity of helminths and subsequent poisoning.
- Meningoencephalitis is a dangerous inflammation of the brain and its membranes caused by bacteria and protozoa.
Different pathogens have their own manifestations and consequences, but most symptoms are common to all helminths.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is made under laboratory conditions. Only in this case, in the presence of worm eggs and their signs in blood or feces, helminthiasis can be confidently diagnosed. However, stool analysis is not always sufficient - certain types of parasites do not appear in it. A special method for determining the presence of worms is a serological blood test for antibodies. The following are used to diagnose helminthiasis:
- bile tests;
- macroscopy (to identify roundworms and fungi);
- muscle tissue biopsy to check for trichinosis;
- X-ray and ultrasound.
Trichinosis is a parasitic disease in which the larvae of the pathogen spread throughout the host and wreak havoc on the organs and central nervous system, then colonize the muscle tissue. Parasites in human muscles gradually create an infiltrate capsule around themselves, and the symptoms of their presence in the body decrease, but by this time they have already caused serious damage to the host's health.
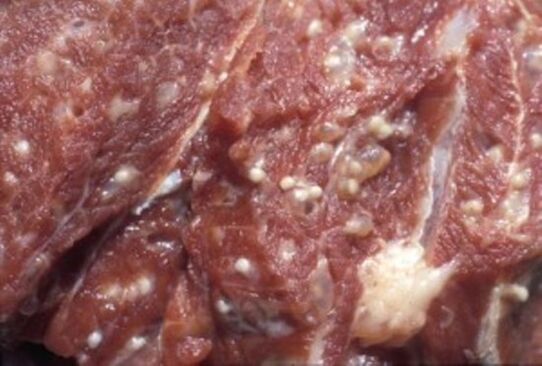
One of the main symptoms is eosinophilia, in which the number of eosinophils in the patient's blood increases sharply. Eosinophils are a subtype of leukocytes that respond to the presence of the smallest foreign body in the circulatory system. In places where parasite larvae accumulate, internal swelling and spots on the skin quickly appear - signs of infiltration. They also remain in sputum and lung fluid.
Since the symptoms of helminthic diseases are extensive and largely overlap with the signs of other diseases, self-diagnosis cannot be completely reliable. There are cases where people have noticed dark threads in their stool after eating bananas, which they have mistaken for worms. All tests should be performed to determine the presence and type of parasites before starting treatment.
Treatment of helminthiasis
Several general rules must be followed when treating parasitic diseases:
- Thorough disinfection of the patient's bedding and the room in which he is staying. Minimize contact, separate containers.
- Strict diet without alcohol. Consumption of carrot juice and birch bud infusion is recommended.
- Observe personal hygiene, frequent hand washing and washing, cleaning of living spaces.
- Monitoring treatment progress and effectiveness.
Modern treatment methods exclude the use of a separate drug, as this does not guarantee full coverage of all types of helminths. Most often, the doctor prescribes an initial drug that weakens the parasites. After 3 days, depending on the patient's age and the severity of the infection, anthelmintic drugs are prescribed. A non-toxic drug from the tetrahydropyrimidine group is prescribed for pregnant women or people who have contraindications to drug treatment.
If it is not possible to consult a doctor, then use folk remedies. The following have a good anthelmintic effect:
- enema of garlic infusion, taking garlic on an empty stomach;
- tansy infusion on an empty stomach, 4 times a day before meals;
- wormwood tincture in alcohol, 3 times a day, 20 mg.
Nowadays, helminth infections are diagnosed and treated in a short time. If you do not neglect the disease and start treatment on time, this will help to avoid complications and reinvasion. Parasitic diseases pose the greatest danger to children: intellectual development slows down, complications appear in the form of chronic diseases and inflammatory processes. It is extremely important that you immediately explain to your child the need to wash hands and observe personal hygiene rules. Adults should also follow other preventive measures.
Prevention of helminthiasis
In addition to personal hygiene, several factors influence the elimination of the cause of worms:
- washing vegetables and fruits in hot water;
- keeping the house clean, regular wet cleaning;
- a balanced diet that provides the body with a sufficient amount of vitamins from all groups;
- checking the condition of pets, annual visits to the veterinarian;
- proper heat treatment of fish and meat;
- fight against insects living in the house;
- refrain from swimming and resting in areas where cattle graze.
Adherence to preventive measures and timely consultation with a doctor in case of infection will help to avoid complications. The correct dosage of drugs prescribed by the doctor will quickly get rid of parasites, and folk remedies can be used in combination with prescribed drugs.






































